Considering recovery of mitochondrial function Part 1: Production of reactive oxygen species
The air we breathe contains 21% oxygen.
Oxygen is a type of radical, but
it rarely reacts with other substances because it has a special molecular structure.
However, oxygen that is taken up from the lungs and delivered to the tissues during respiration
can be transformed into an unstable form that is more reactive under mild conditions in vivo.
These unstable oxygen species are called reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Reactive oxygen species have
the property of reacting with other substances and trying to become stable.
Therefore,
reactive oxygen species may react with proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, etc., and
oxidize and denature them.
Since reactive oxygen species are based on oxygen,
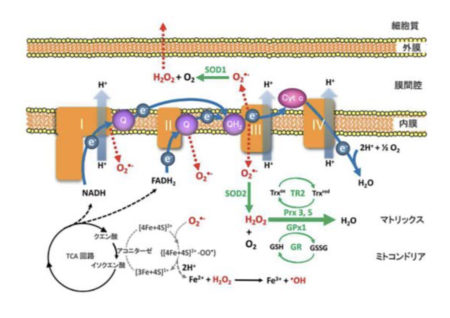
mitochondria, which consume a large amount of oxygen, inevitably generate reactive oxygen species.
In fact,
more than 90% of the oxygen in the body is consumed by mitochondria,
so most of the reactive oxygen species are thought to be derived from mitochondria.
The most important function of mitochondria is
to use their oxygen to make energy ATP for growth and survival.
It is inevitable that
0.1-2% of the oxygen will be converted to reactive oxygen species during this process.