If you think you may have mild cognitive impairment (MCI) Part 2: Apolipoprotein
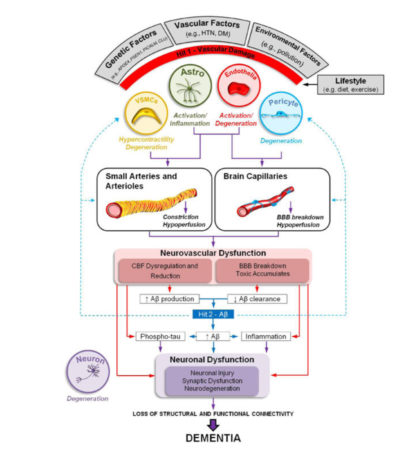
The rapid increase in the number of people with dementia has become a major social problem.
The onset of Alzheimer’s disease, which accounts for the majority of dementia,
is caused by lifestyle (diet, exercise, etc.) and related lifestyle diseases (diabetes, hypertension, etc.).
Environmental factors and genetic factors, both factors are believed to be involved.
Apolipoprotein (Apo) is a protein
that binds to lipoproteins and participates in lipid metabolism.
There are three genetically determined types of ApoE (E2, E3, and E4),
and having E4 is an established risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease.
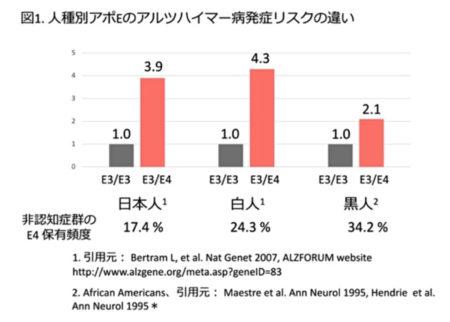
In Japanese,
it has been reported that
the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease is
approximately 3.9 times higher in people with apoE E4 (E3/E4) than in non-carriers (E3/E3) (Fig. 1).
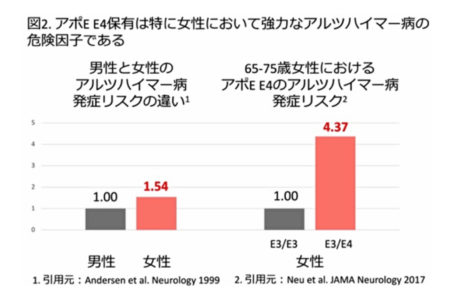
ApoE E4 carriage is also known to be a strong risk factor for
developing Alzheimer’s disease, especially in women (Fig. 2).
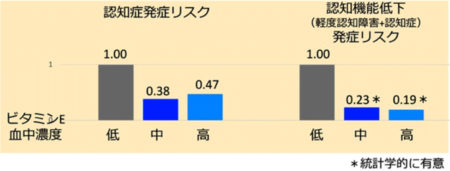
There is currently no established method to reduce the risk of cognitive decline
in ApoE E4 carriers, a strong genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease.
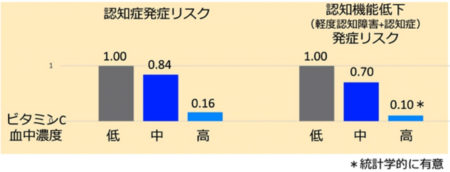
A recent study at the Department of Neurology, Kanazawa University Hospital,
suggests that these risks can be prevented by increasing blood levels of vitamin C and vitamin E.
The fact that vitamin C was suggested to reduce the risk of cognitive decline
in women with ApoE E4 also has a significant social impact.
Regarding vitamin E,
the results were similar to those of previous studies,
supporting the effect of vitamin E intake in suppressing cognitive decline in men without apoE E4.